Late Model

Bully Dog Technologies, located in Aberdeen, Idaho, designs and develops some great bolt-on power products for the diesel aftermarket. Creating these pieces involves literally hundreds of hours in R&D and design work with some of the brightest engineers and technicians around. But, as you can imagine, it’s fun work.
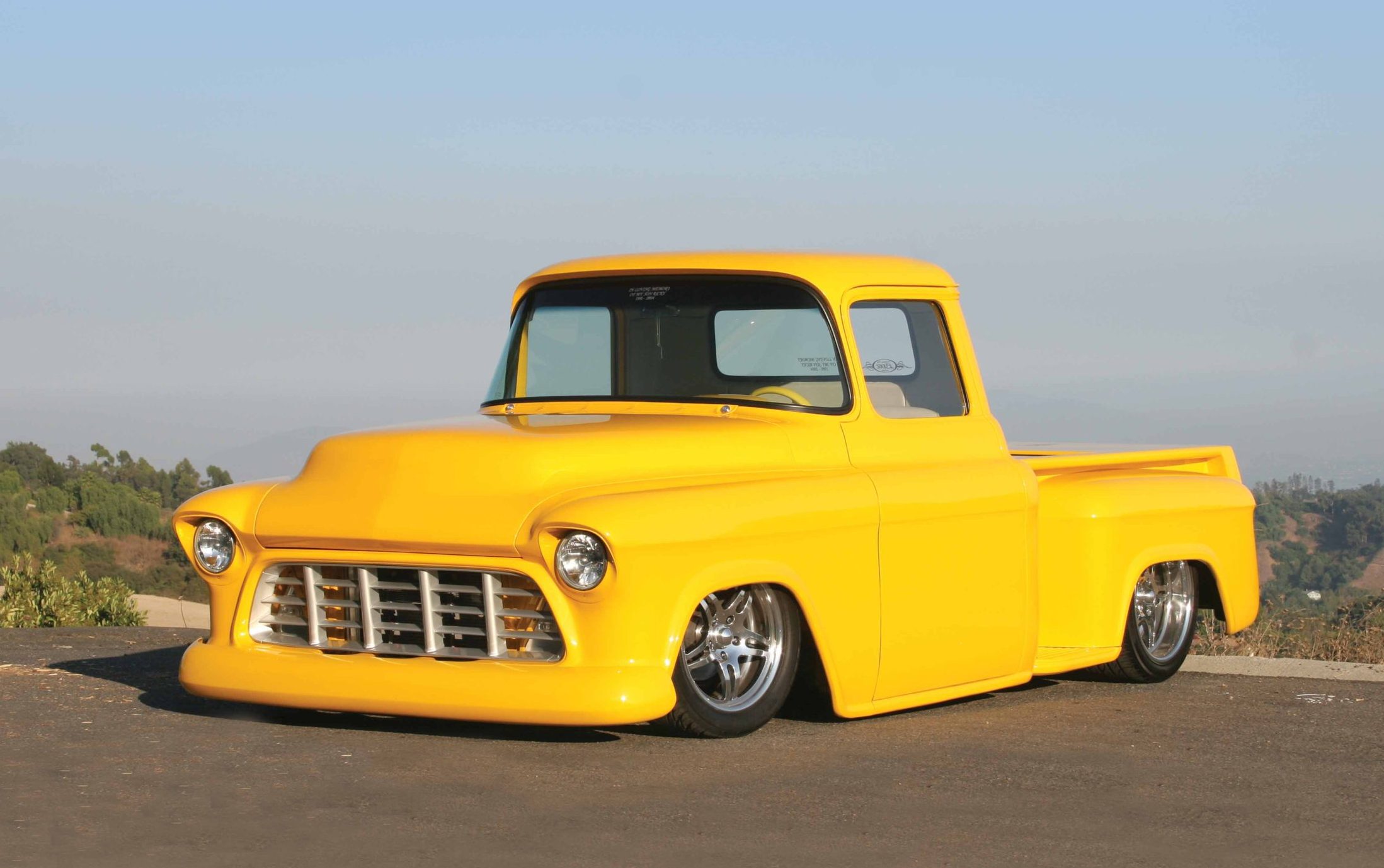

When Ricardo Lopez began building this 1955 Chevy he had some help, as well as a plan. In the beginning, this little Chevy pickup was to provide an excellent chance for Ricardo to spend some time with his son, Ricky, and to be able to show the boy some of the tricks that he had learned over the many years he had worked as a customizer, bodyman and painter. As owner of Paint By Lopez in Compton, California, Ricardo had hopes of his boy taking over for him in the years to come, maybe even calling the shop Paint By Lopez & Son. Unfortunately, Ricky was taken from Ricardo and his wife, Monica, in a freak accident. At first Ricardo was going to sell the truck, as the sight of it was almost too much to bear. But upon reflection he changed his mind. Ricardo thought that finishing the project was not only a perfect way to work through his grief, but it would also give him a chance to feel connected to the son he had lost. When the Chevy was completed, it would be a way to honor Ricky’s memory.

It can be argued that one of the best mods you can make to an LS-based or Gen III motor is a camshaft change. With the number of aftermarket companies making many different types, a good cam can be found for anywhere from $300 to $1,000, depending upon what type of power you want to make and how sophisticated the cam package is. Because 99.99 percent of all vehicles on the road today are computer controlled, most aftermarket companies are able to suggest whether a new tune will be necessary or if the stock one will suffice. But with so many different options out there, it can be quite confusing as to which is the right one for you.
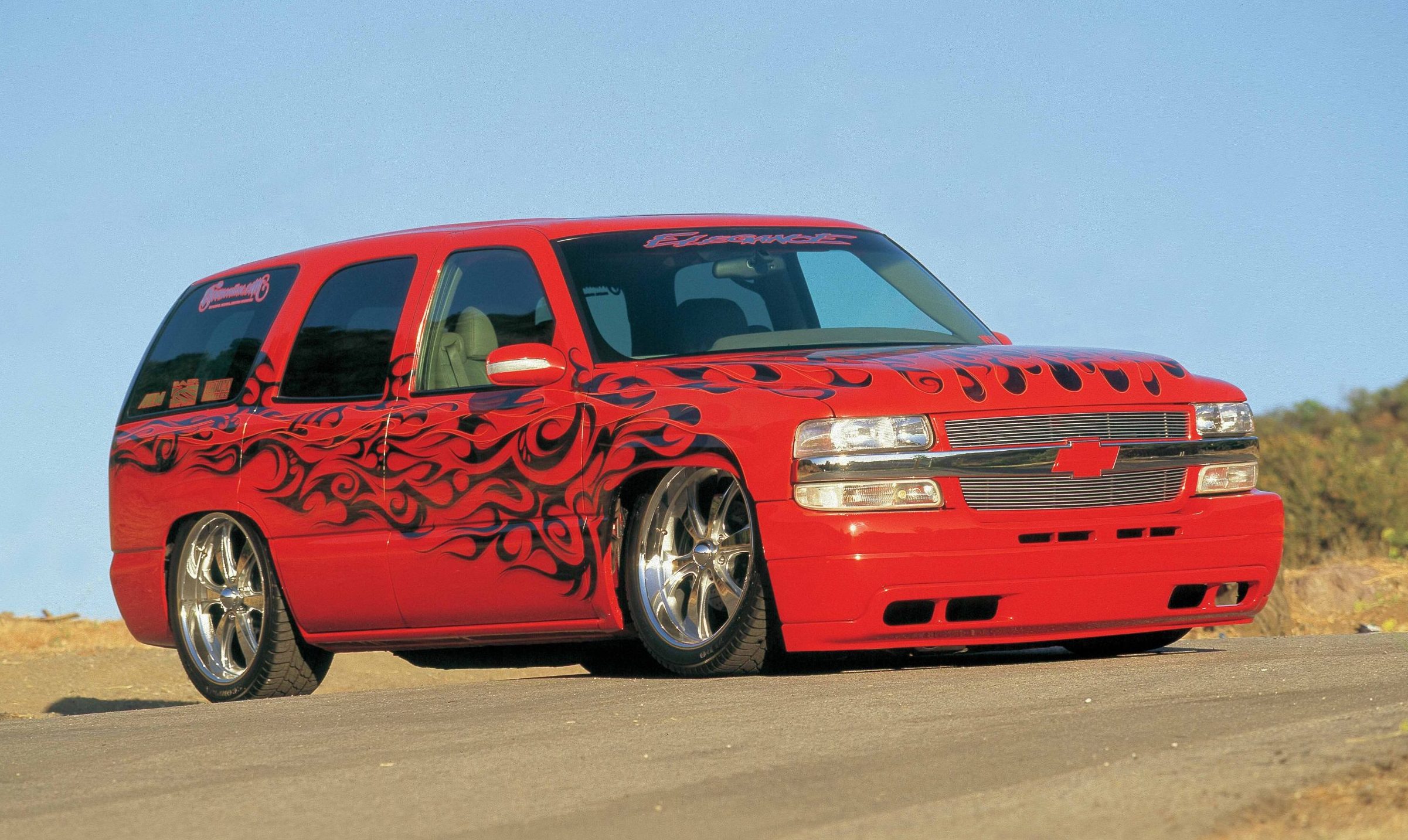

Though only 27 years of age, Mike MacKellar has built an impressive résumé as not only a truck builder, but also a businessman. As the owner of a financial services company, MacKellar is well aware of how much things cost, and it seems that he spared little expense when he set about building this 2001 Chevrolet Tahoe. He also knew just how he wanted his latest project to be.
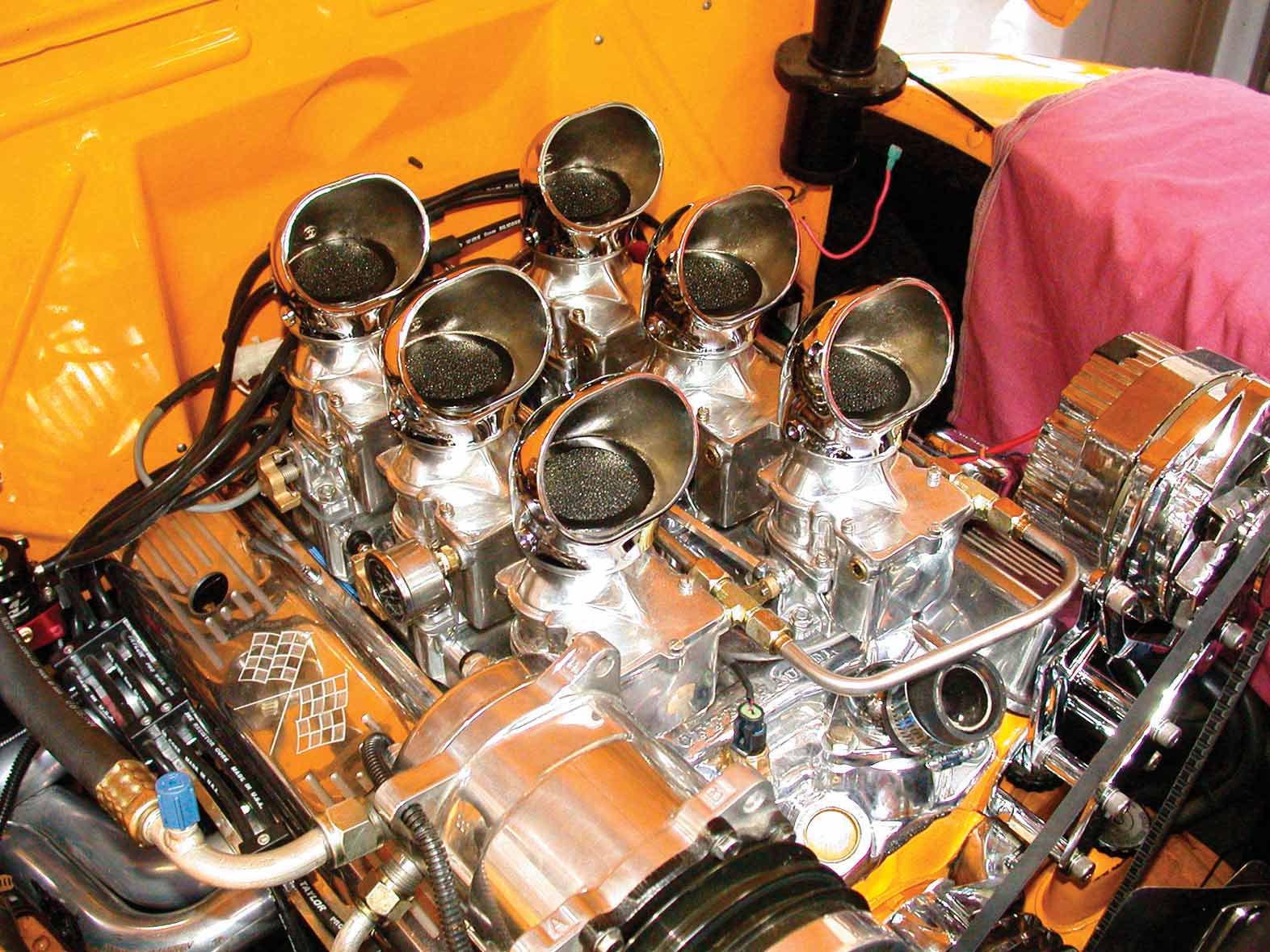

Those who longed for their engines to look as they did back in the old days of multiple-carb setups were out of luck. Cool as they were to look at, there are lots of reasons why the multi-carb setup fell out of favor, and most of them had to do with the fact that they were a bear to sync. The advent of the four-barrel carb was the death for these systems, though the purists among us prayed for a breakthrough. Thanks to Ken Farrell and his company, Retro Tek, those prayers have been answered. Farrell started off converting old mechanical fuel injection systems (Hilborn & Enderle) when the first aftermarket EFI systems became available. His new system, which uses the latest in EFI mated together with the classic Stromburg 97 design, came about when Farrell saw that there was interest in the benefits of EFI, but he also knew that they were lacking in the looks department. The idea was simple take the best aspects of both and add them together.
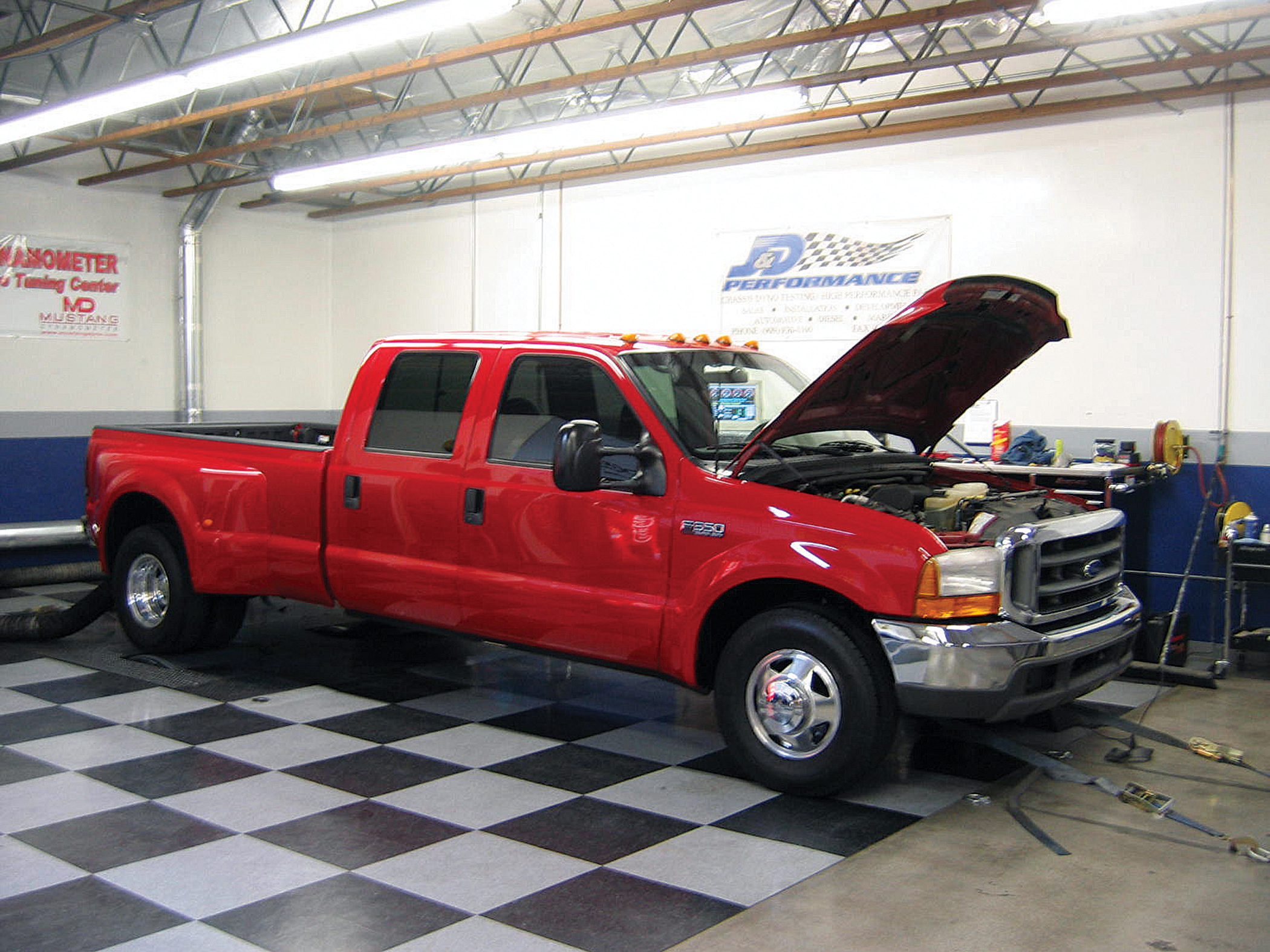

Like their diesel counterparts, gas-powered truck owners are always looking for ways to give their vehicles even more power and better mileage. To find out what kind of power options there are for gas-powered trucks, we went to J&D Performance in Ontario, California. We’ve seen what kind of power and performance the guys at J&D can make in a diesel-powered truck, so we figured we’d follow along as they wrenched more power out of a common gas-powered truck. After a quick phone call, we were set. The guys at J&D had a customer’s stock 1999 Ford F-350 dualie with a 6.8-liter V-10 ready for buildup. Here’s how it went.
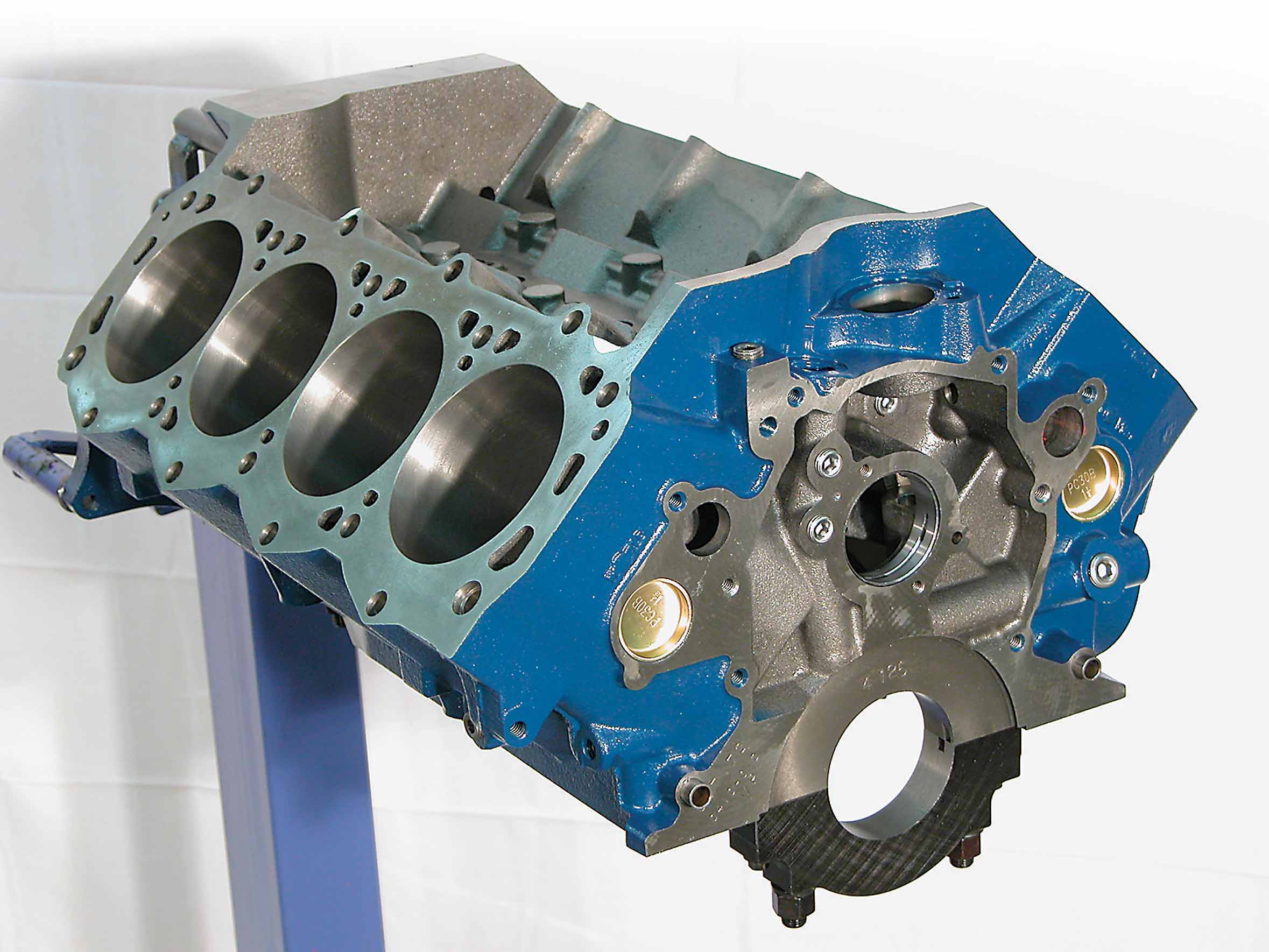

Ford engines are hot, and everyone—even non-Ford guys—are talking about it. The small-block Ford is an awesome package that is made even more awesome by Ford Racing and aftermarket parts. It has continually gained popularity as a high-performance buildup, as a Ford In A Ford engine transplant and as a replacement performance engine for vehicles that were optioned as such but were less equipped when new. With all of this activity surrounding the small-block Ford engine, it is safe to say that it is quickly becoming the small block of choice.
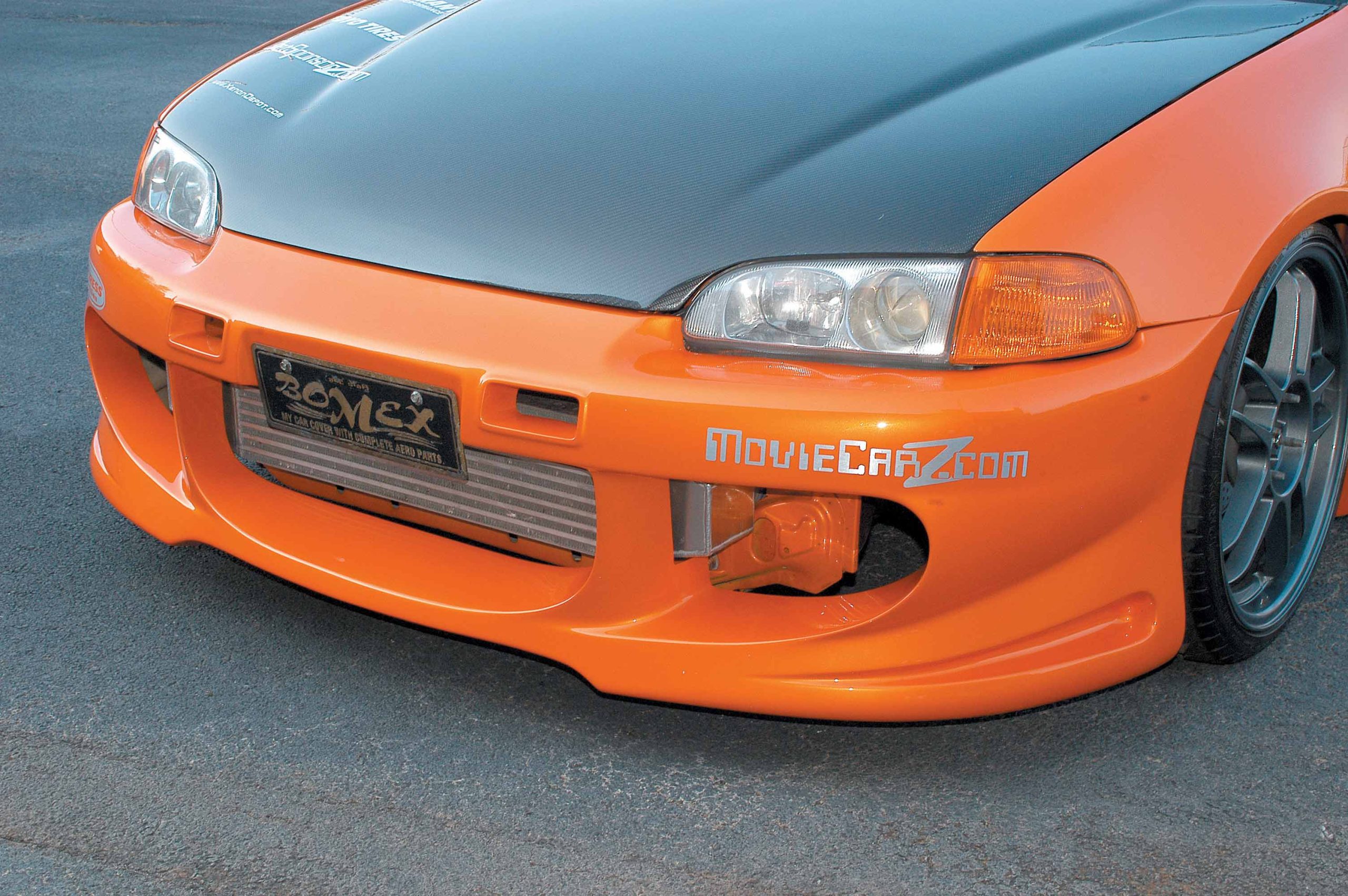

Discover the remarkable journey of Ben Bodor’s Civic transformation as it defies expectations, emerging as a formidable contender in the U.S. car scene. From its origins in Canada to its stunning evolution, follow the Bodor brothers’ quest for automotive excellence in this gripping tale of innovation, carbon fiber craftsmanship, and the pursuit of perfection.
Everyone wants a killer stereo that rocks. You can’t just roll out in your car without something fabulous to listen to. The factory equipment just won’t work for those who demand more, especially if you are trying to show off. You have to be able to turn up the music and be heard—it’s all part of the game. If you’re going to roll, you know the rules: you have to roll hard and that means your entire stereo system has to be up to the task. Nothing is worse than blasting a stereo and hearing everything rattle and shake. That’s a huge no-no. There is a simple solution to this problem, however. To do a proper stereo installation, you must first lay a solid foundation. The first layer of this foundation is called sound damping or sound control.

Driven Racing Oil developed the original high zinc, petroleum and low detergent break-in oil over twenty years ago. Break in oil is a specialty oil that reduces wear and contaminates when breaking in a new high-performance engine. It provides controlled friction for your piston rings and incredible protection that helps your camshafts break in properly.










